Fire Safety Challenges in Singapore’s Industrial Sector and How to Overcome Them
Introduction
Singapore’s industrial sector is a cornerstone of the nation’s economy, encompassing manufacturing, logistics, and petrochemicals. However, the presence of hazardous materials, high-energy equipment, and complex operations makes fire safety a significant concern. Recent fire incidents have underscored the need for proactive measures to mitigate risks and protect lives, assets, and business continuity.
Common Fire Safety Challenges in the Industrial Sector
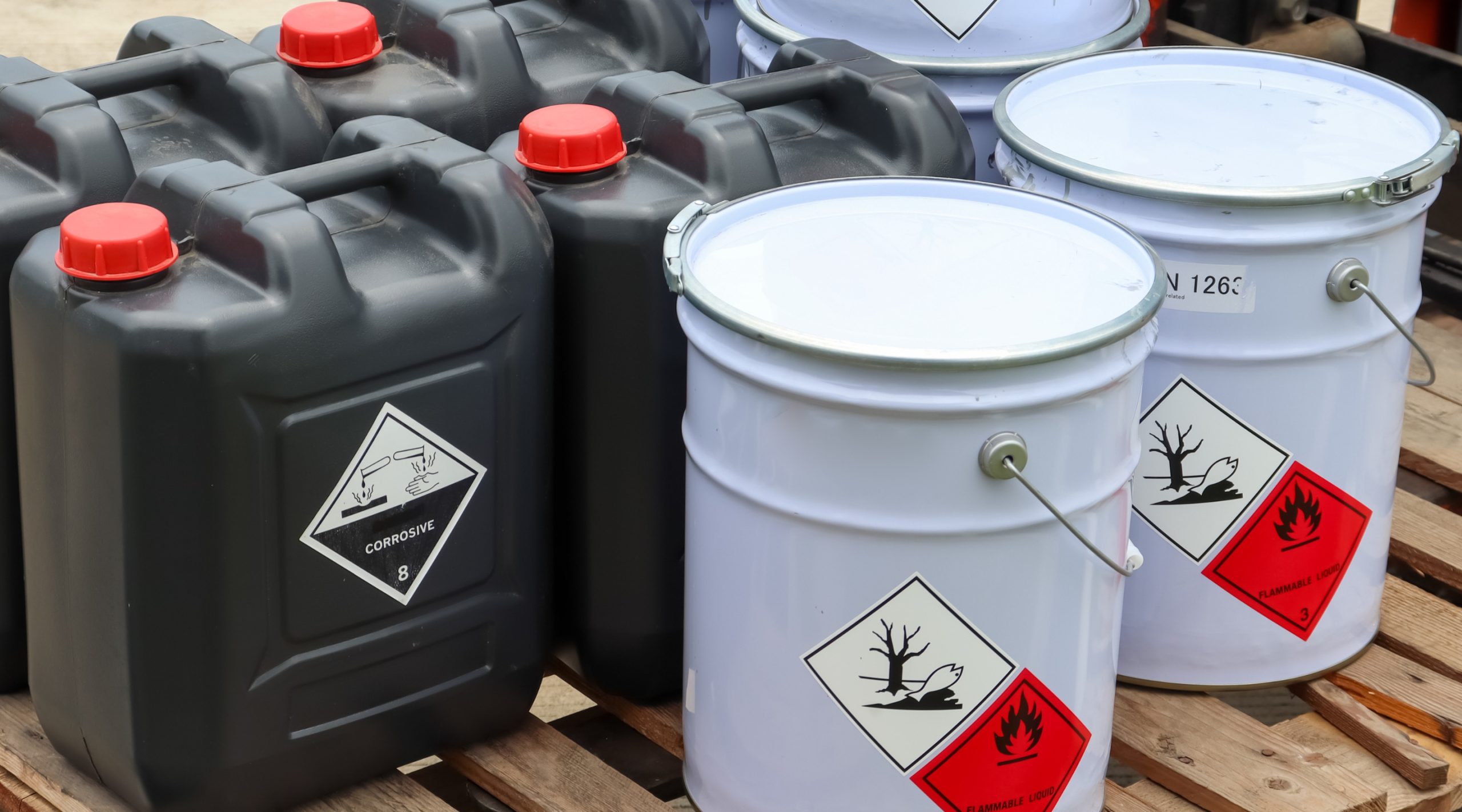
1. Storage and Handling of Flammable Materials
Industries dealing with chemicals, fuels, and other combustible substances face heightened fire risks. Improper storage, lack of ventilation, and accidental spills can lead to rapid fire outbreaks.
Solution: Implement stringent hazardous material management protocols, including proper labeling, fire-resistant storage units, and regular safety drills.
2. Aging Infrastructure and Equipment Malfunctions
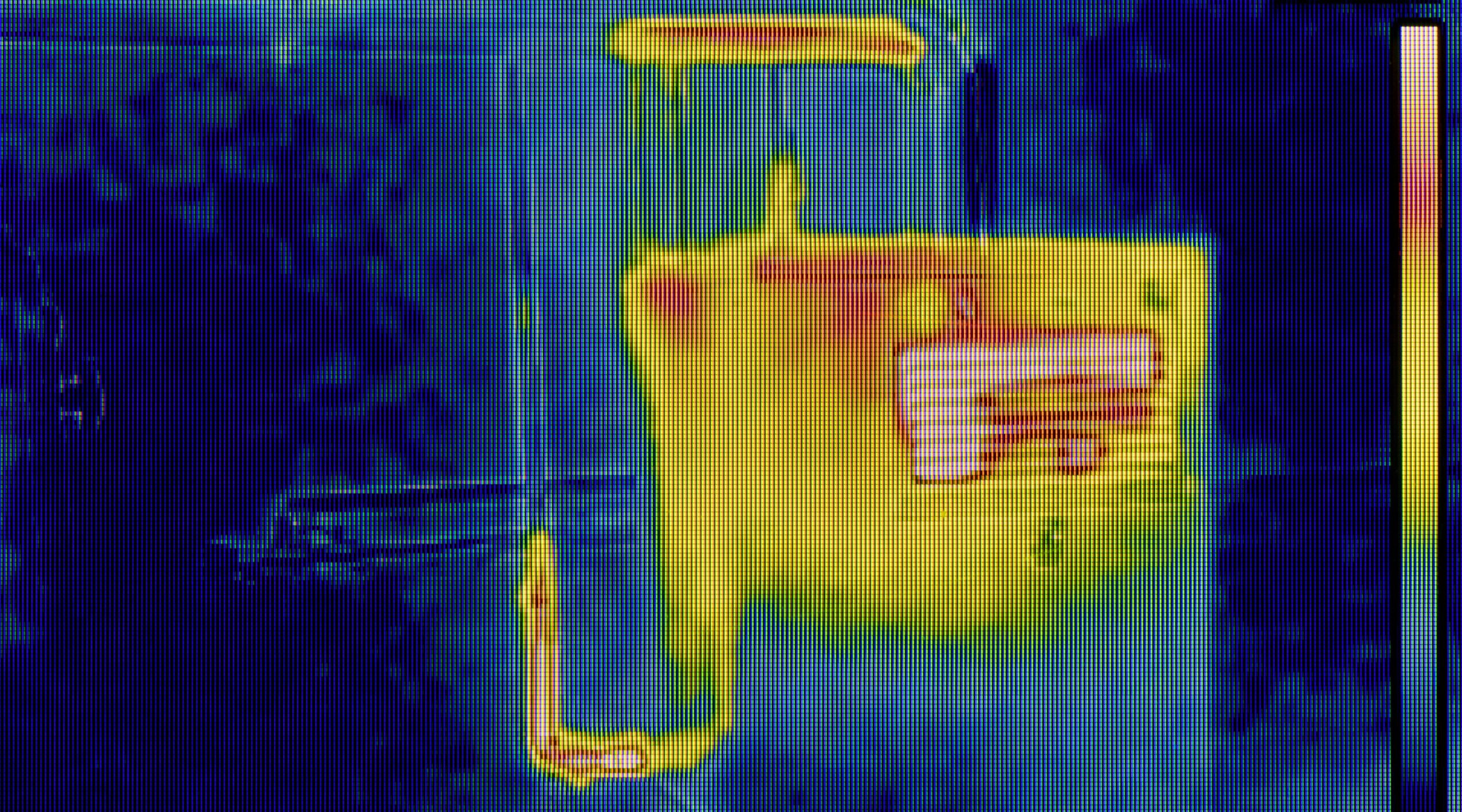
Many industrial facilities operate with aging electrical systems, outdated machinery, and corroded pipelines, increasing the likelihood of electrical fires and mechanical failures.
Solution: Conduct regular inspections, upgrade old equipment, and adopt predictive maintenance technologies to identify potential failures before they occur.
3. Lack of Fire Safety Awareness Among Employees
Despite regulations, some employees may not be adequately trained in fire prevention and emergency response, leading to slow or ineffective reactions during a fire.
Solution: Provide ongoing fire safety training programs, conduct routine fire drills, and establish clear emergency evacuation plans.
4. Insufficient Fire Suppression Systems
Outdated or inadequate fire suppression systems can fail to control fires effectively, especially in high-risk areas such as chemical storage rooms and electrical panels.
Solution: Invest in modern fire suppression technologies, such as automated sprinklers, gas-based suppression systems, and high-performance fire extinguishers tailored for industrial environments.
5. Non-Compliance with Fire Safety Regulations
Strict fire codes exist in Singapore, but non-compliance due to cost constraints, oversight, or lack of expertise can lead to severe penalties and increased fire hazards.
Solution: Work closely with regulatory bodies like the Singapore Civil Defence Force (SCDF) to ensure compliance with the Fire Code, perform periodic audits, and integrate fire safety into overall risk management strategies.
Strengthening Fire Safety Measures in Industrial Facilities
Adoption of Smart Fire Detection Technologies
Smart sensors, AI-driven fire detection, and IoT-enabled monitoring systems provide real-time alerts and predictive insights, allowing early intervention before fires escalate.
Fire Safety Integration in Facility Design
Incorporating fire-resistant materials, compartmentalization, and strategically placed escape routes during facility design significantly reduces fire spread and enhances evacuation efficiency.
Emergency Response Coordination
A well-prepared emergency response plan, including collaboration with local fire departments, ensures quick action during fire incidents. Regular coordination drills with external emergency services improve preparedness.
Encouraging a Safety-First Culture
Management must prioritize fire safety by fostering a culture where employees proactively identify hazards, report unsafe practices, and follow established safety protocols.
Conclusion
Fire safety remains a dynamic challenge in Singapore’s industrial sector, requiring a multifaceted approach that combines regulatory compliance, employee training, and technological advancements. By addressing vulnerabilities and fostering a strong fire prevention culture, businesses can significantly reduce fire risks, ensuring the safety of their workforce and the resilience of their operations.