How IoT is Transforming Fire Safety in Singapore
Introduction
Fire safety has always been a top priority in urban environments like Singapore, where high-rise buildings, industrial facilities, and commercial hubs dominate the landscape. With advancements in technology, the Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing how fire hazards are detected, prevented, and managed. By leveraging smart sensors, real-time data analytics, and automated response systems, IoT is significantly enhancing fire safety measures, reducing response times, and minimizing property damage and human casualties.
The Role of IoT in Fire Prevention
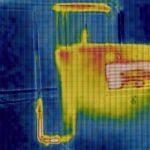
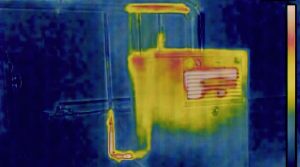
Prevention is the first line of defense against fire-related incidents. IoT-enabled fire safety solutions proactively identify potential hazards before they escalate. Smart fire detection systems, equipped with advanced sensors, continuously monitor environmental conditions such as temperature, smoke levels, and gas leaks. Unlike traditional fire alarms that activate only after a fire has started, IoT-based solutions provide early warnings, allowing property managers and emergency services to intervene promptly.
For example, smart smoke detectors and thermal sensors installed in buildings can communicate with central monitoring systems. These devices can differentiate between normal activities, such as cooking, and potential fire outbreaks, reducing false alarms and ensuring swift, accurate responses when necessary.
Real-Time Monitoring and Predictive Analysis
One of the most significant benefits of IoT in fire safety is real-time monitoring. IoT-connected fire safety devices continuously transmit data to cloud-based platforms, where artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms analyze trends and predict risks. This predictive analysis helps identify patterns that may indicate potential fire hazards, such as overloaded electrical circuits, equipment overheating, or gas leaks.
For instance, in industrial settings, IoT-based predictive maintenance systems can monitor machinery and electrical infrastructure to detect unusual heat levels or malfunctions. By addressing these issues proactively, businesses can reduce the likelihood of fire incidents and costly downtime.
Automated Emergency Response Systems
In the event of a fire, every second counts. IoT-driven automation can significantly improve emergency response efficiency by integrating smart fire alarms, sprinkler systems, and emergency exit controls. When a fire is detected, IoT-enabled systems can automatically activate fire suppression mechanisms, unlock escape routes, and notify emergency responders in real time.
Singapore’s urban landscape, with its complex infrastructure and densely populated areas, benefits greatly from such automation. Smart building management systems can guide occupants to the safest evacuation routes using digital signage, mobile alerts, and voice-assist technology, reducing panic and ensuring a coordinated evacuation.
Enhancing Fire Safety in Smart Cities
Singapore’s Smart Nation initiative has been driving the adoption of digital technologies, including IoT, to improve public safety. The integration of IoT into fire safety aligns with this vision by providing a city-wide network of interconnected fire monitoring systems. Government agencies and emergency services can access real-time data from buildings, public spaces, and transportation hubs to respond more efficiently to fire emergencies.
For example, Singapore’s Housing and Development Board (HDB) has explored the use of IoT-based fire detection in residential areas. Smart fire alarms connected to the cloud can immediately alert both residents and the Singapore Civil Defence Force (SCDF), ensuring faster response times and reducing fire-related casualties.
Future of IoT in Fire Safety
As technology continues to evolve, IoT’s role in fire safety will expand further. Future innovations may include AI-powered drones for real-time fire assessments, smart firefighting robots, and enhanced predictive analytics for fire risk assessment. The integration of 5G connectivity will also enable faster data transmission, improving the efficiency of IoT-driven fire safety solutions.
Businesses, property managers, and government agencies in Singapore must embrace these advancements to enhance fire safety strategies. By investing in IoT-enabled fire prevention and response systems, they can protect lives, reduce economic losses, and contribute to a safer urban environment.
Conclusion
The implementation of IoT in fire safety is reshaping how Singapore approaches fire prevention, monitoring, and emergency response. Through smart sensors, real-time data analysis, and automated response systems, IoT enhances safety measures and minimizes the risks associated with fire incidents. As Singapore continues to embrace smart city initiatives, integrating IoT into fire safety will play a crucial role in safeguarding lives and infrastructure, ensuring a more resilient and secure future.